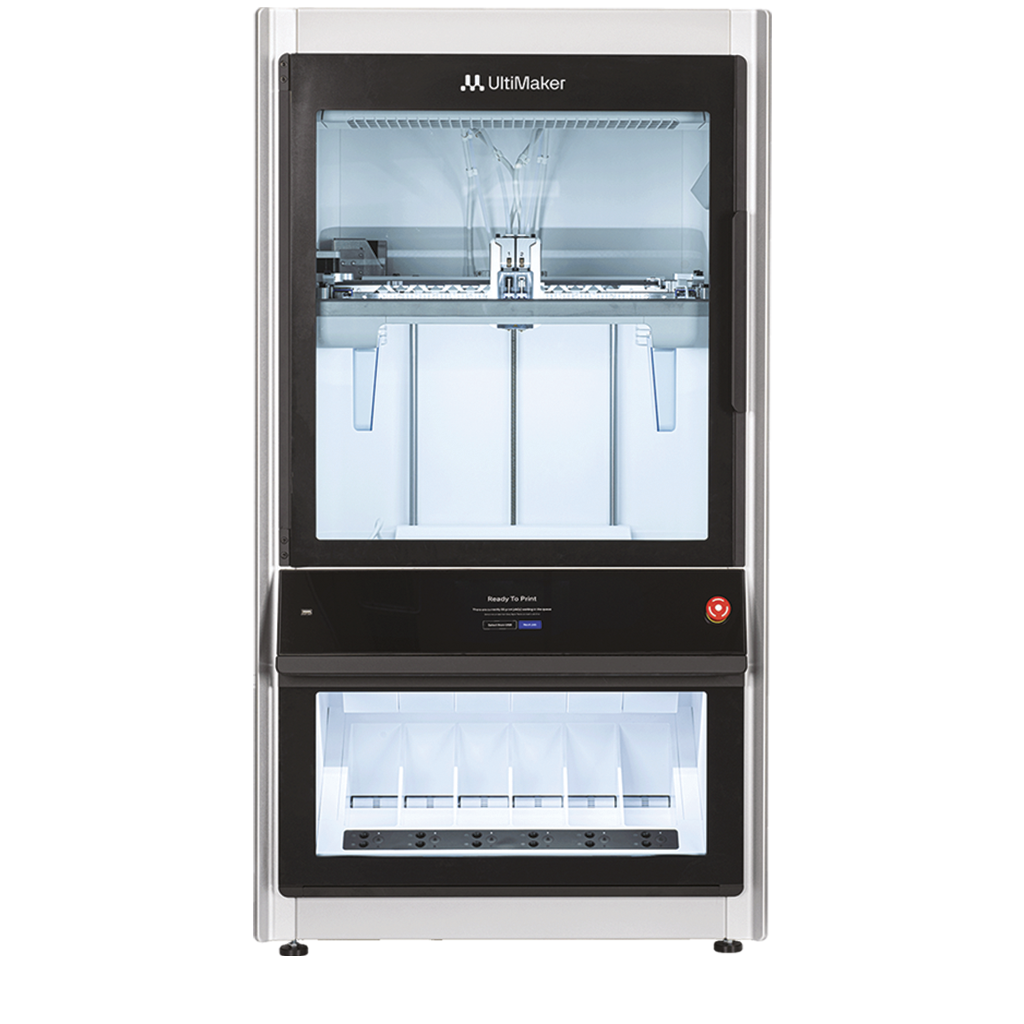
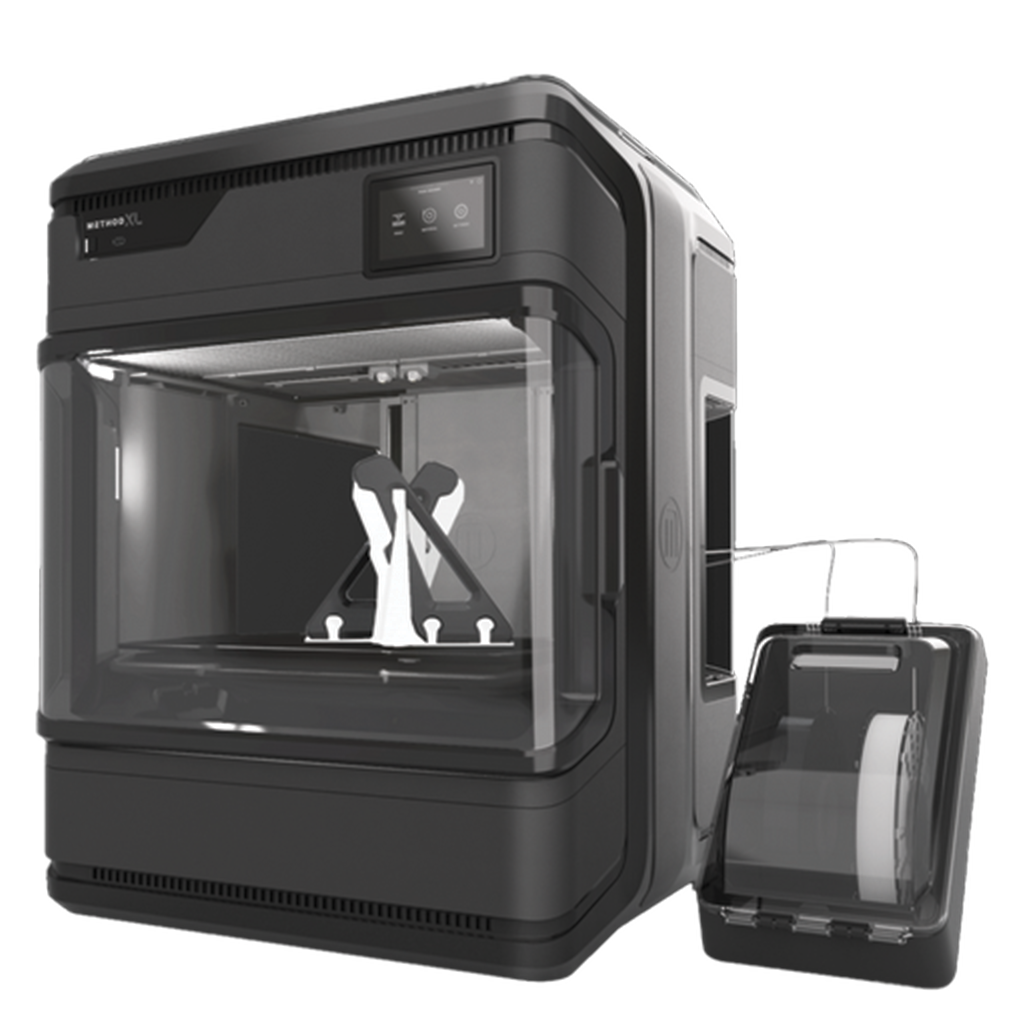
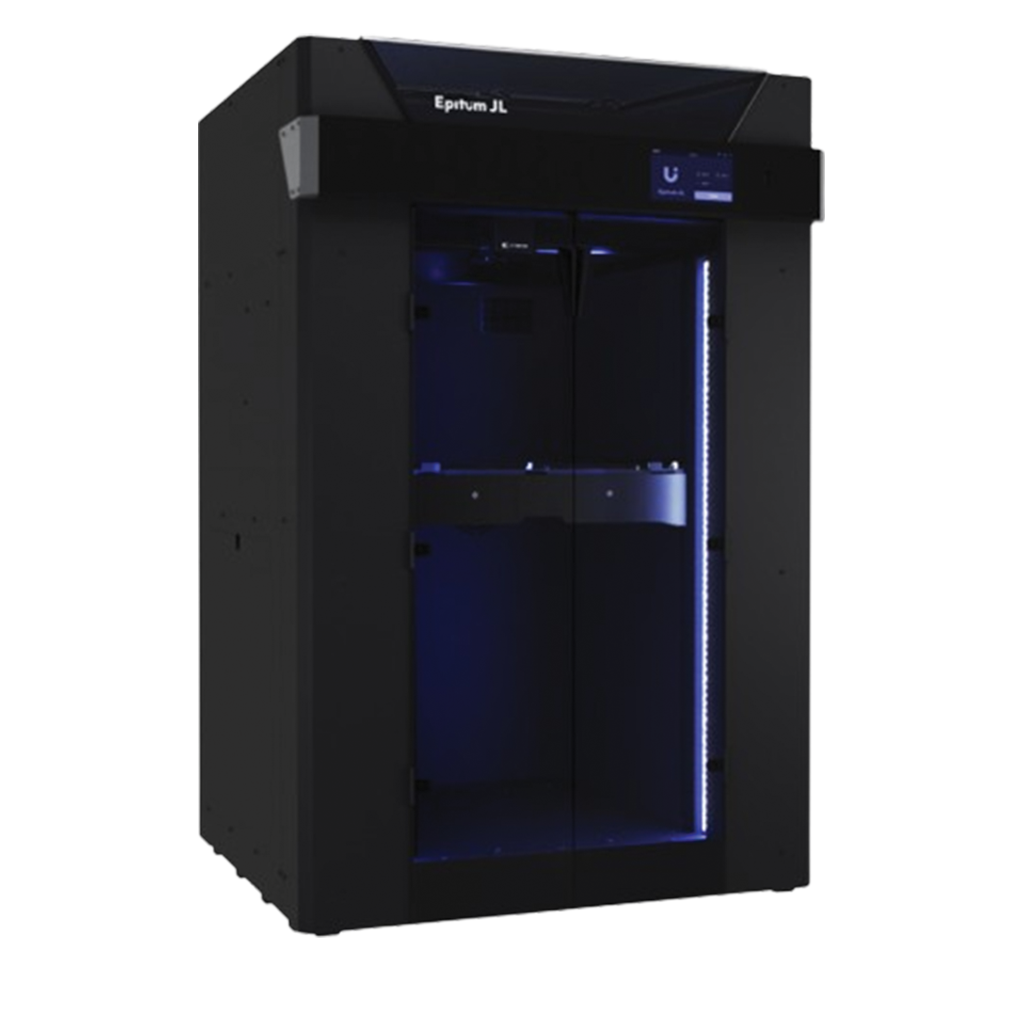
Industrial Grade 3D Printer
Industrial-grade 3D printers represent the forefront of additive manufacturing, particularly in fabricating objects with composite materials. Unlike conventional printers limited to single-material printing, these systems integrate multiple materials, yielding parts with superior mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. This advancement in additive manufacturing technology broadens the scope of applications and enables the production of high-performance components across industries, ready for deployment on the factory floor.
FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication)
FFF commonly stands for “Fused Filament Fabrication,” which is a 3D printing process also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). In this method, a thermoplastic filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. It’s a popular and accessible technique used in various industries for rapid prototyping, manufacturing, and DIY projects.

LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
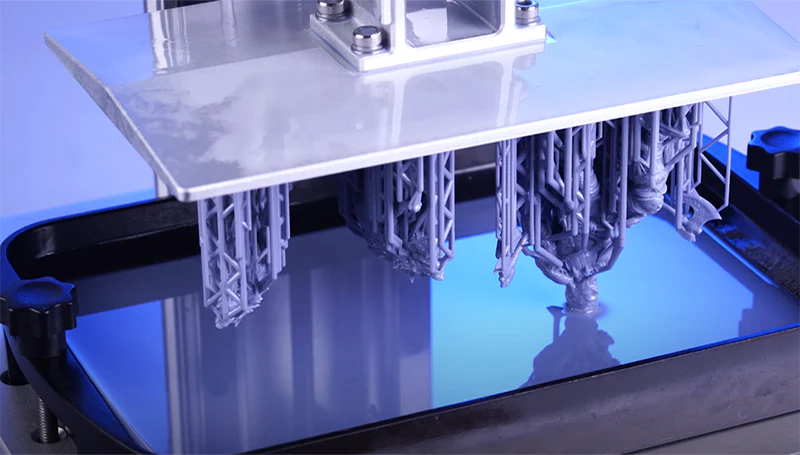
LCD 3D printing, also known as Masked Stereolithography (MSLA), is a type of resin-based 3D printing technology. In LCD 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured layer by layer using an LCD screen to mask the UV light, solidifying the resin where it’s exposed to light.

SLA (Stereolithography)
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing is an advanced additive manufacturing technique used for creating prototypes and intricate models. It utilizes a liquid photopolymer resin as the print material, contained in a reservoir called the resin tank. The process involves digitally slicing a 3D model into layers, with a UV laser selectively solidifying each layer on the resin surface. SLA yields high-detail objects with precise geometry, making it favored in industries requiring accuracy and complexity.
PRECISE 3D Hub
DIRC Warehouse, W4-D1 Dubai Investment Park - 2, Dubai - United Arab Emirates
sales2.solution@preciseme.com
Contact Number
+971 54 307 2749











